Columns
Widening trade deficits increase external financial vulnerability
View(s): Progressively increasing trade deficits have been a root cause for the country’s weak external finances. The reduction of the trade deficit is crucial to generate a balance of payments (BOP) surplus to reduce foreign borrowing and minimize external financial vulnerability.
Progressively increasing trade deficits have been a root cause for the country’s weak external finances. The reduction of the trade deficit is crucial to generate a balance of payments (BOP) surplus to reduce foreign borrowing and minimize external financial vulnerability.
BOP surplus
A significant balance of payments (BOP) surplus is necessary to avoid further foreign borrowing at high cost to meet foreign debt servicing obligations. Foreign borrowing increases foreign indebtedness, weakens external finances and drives the country into a foreign debt trap.
Trade deficit
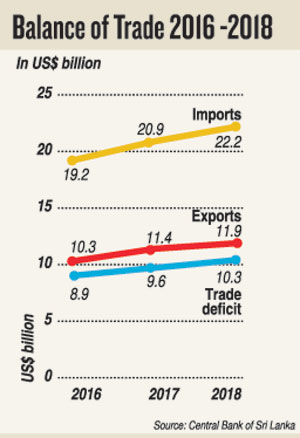
A lower trade deficit is essential to achieve a BOP surplus. The trade deficit expanded in the last three years, to reach a massive US$ 10.3 billion in 2018. This widening of the trade deficit was despite a 15 percent increase in exports between 2015 and 2018. Exports increased from US$ 10.3 billion in 2016 to US$ 11.9 billion in 2018. A much lower trade deficit is crucial to achieve a BOP surplus.
Although exports increased by 10.2 percent in 2017 and by 4.7 percent in 2018, the trade deficit increased from US$ 8.9 billion in 2016 to US$ 9.6 billion in 2017 and to US$ 10.3 billion last year. This is due to a higher increase in imports than exports.
 Increase in imports
Increase in imports
The widening of the trade deficit was due to imports increasing much more than exports. Between 2016 and 2018 imports grew by as much as US$ 3 billion compared to a growth of exports by only US$ 1.6 billion.
In 2018 imports were nearly twice the country’s exports: imports were 84 percent more than exports. Last year’s imports of US$ 22.2 billion compared to exports of only US$ 11.9 billion. A reduction in imports is vital in reducing the trade deficit.
Persistent feature
Imports growing by a much higher amount than exports have been a chronic feature of the country’s external trade. While exports grew by US$ 0.6 billion in 2017, imports grew by US$ 1.7 billion. Similarly, in 2018 when exports grew by 0.5 billion, imports grew by 1.3 billion to increase the trade deficit to US$ 10.3 billion from US$ 9.6 in 2017.
Export growth
The progressive growth in exports has been a notable feature of the last few years. The increase in exports was mainly in industrial exports and sea fish. Agricultural export earnings fluctuated.
Industrial exports that were US$ 7.9 billion in 2015 increased to US$ 9.3 billion in 2018. This 15.6 percent increase in three years is a noteworthy achievement. In contrast, agricultural export earnings during this period fluctuated. They increased by 19 percent in 2017 but fell by 6.7 percent in 2018. Agricultural export earnings were about 13 percent higher in 2018 compared to 2016.
 European Union
European Union
The removal of the ban on fresh fish exports, as well as the restoration of the GSP plus concession, has been important in boosting exports. On the other hand, agricultural exports have not fared too well as the demand for the country’s main agricultural export tea has fluctuated and production too has declined, In 2018 tea export earnings fell by 6.6 percent. The exportable surpluses of most agricultural commodities have been sluggish.
External vulnerability
A root cause for the country’s external vulnerability is the persistent and chronic trade deficits. The large trade deficits result in ether a balance of payments deficit or only a small BOP surplus. BOP surpluses have been achieved when workers’ remittances, earnings from tourism and other services and capital inflows exceed the trade deficit.
If the trade deficit is not contained to achieve a significant balance of payments surplus, foreign borrowing is needed to meet foreign debt obligations and finance development expenditure. Further foreign borrowing would increase the currently large foreign debt and enhance the country’s external financial vulnerability. This is the rationale for decreasing the trade deficit.
The larger the trade deficit, the lesser the likelihood of a BOP surplus of significance. In 2018 the trade deficit of US$ 10.6 billion was offset by workers remittances of US$ 6.7 billion and tourist earnings of US$ 4.1 billion that amounted to 10.8. This was only a small BOP surplus. Had the trade deficit been around US$ 8 billion, then the BOP surplus on the current account would have been about US$ 3 billion.
Importance
This underscores the importance of reducing the trade deficit. A lower trade deficit is imperative to achieve a balance of payments surplus to reduce the country’s external financial vulnerability as further foreign borrowing at high cost for foreign debt servicing would weaken the external finances and drive the country into a foreign debt trap.
Summary and conclusion
The trade deficit has to be reduced to achieve a significant balance of payments surplus to enhance the country’s foreign reserves to meet foreign debt obligations and finance development expenditure, Further borrowing would increase the currently large foreign debt and aggravate the country’s external financial vulnerability.
The trade deficit has to be reduced by both an increase in exports and the curtailment of non-essential imports and import substitution. While export growth has been impressive, imports have increased to widen the deficit to a large amount. Therefore the reduction of non- essential imports is vital while a further expansion of exports must also be achieved.


Leave a Reply
Post Comment