Columns
Prospect of lower trade deficit strengthening external finances in 2019
View(s): The country’s external financial vulnerability remains a serious concern despite the Central Bank’s assurance that the country’s debt repayment obligations can be met this year and that foreign reserves are expected to be US$ 6.7 billion at the end of the year.
The country’s external financial vulnerability remains a serious concern despite the Central Bank’s assurance that the country’s debt repayment obligations can be met this year and that foreign reserves are expected to be US$ 6.7 billion at the end of the year.
On the other hand, if the decline in the trade deficit in the first quarter of this year continues during the remaining months, a sharp reduction in the trade deficit could result in a significant balance of payments surplus that would strengthen the external finances.
Important
It is of utmost importance that this declining trend in imports continues in the next nine months to reduce the trade deficit to around US$ 8 to US$ 8.5 billion that could improve the balance of payments to achieve a significant surplus. This is especially important as the insecure conditions in the country and geopolitical factors are likely to decrease tourist earnings, foreign investments and workers’ remittances that are significant foreign exchange earnings.
 External vulnerability
External vulnerability
The country’s external vulnerability is due to the large foreign debt and debt repayment obligations. The foreign debt of the country is likely to rise to about US$ 55 billion at the end of this year. This is mainly due to the need to borrow to repay outstanding debt obligations of around US$ 3 billion during the rest of the year.
This foreign debt of over 50 percent of GDP is too high. Foreign debt repayments have been nearly 30 percent of merchandise export earnings in recent years. Consequently the country is in a vulnerable position, especially when facing external and internal shocks.
BOP surplus
Balance of payments (BOP) surpluses have been small owing to persistent large trade deficits. These small BOP surpluses have been inadequate to replenish the foreign reserves. A lower trade deficit this year could result in a higher BOP surplus.
This can only be achieved by a much lower trade deficit than last year’s US$ 10.3 billion and the previous year’s US$ 9.6 billion. The trade deficit must be brought down to about US$ 8 to 8.5 billion to make a dent in the external financial position.
Can this be achieved this year?
There is a prospect of a reduced trade deficit this year, if the decline in the trade deficit to US$ 1.7 billion in the first quarter and the sharp decrease in the March trade deficit continues.
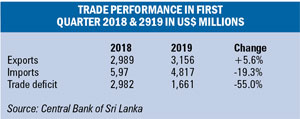
In the first quarter of 2019, the trade deficit contracted to US$ 1.66 billion from US$ 2.98 billion in the first quarter of 2018.This 55 percent decrease in the trade deficit was brought about by a 5.6 per cent increase in export earnings and by a reduction in import expenditure by as much as 19.3 per cent. This trend must continue to achieve the desired BOP surplus.
March trade balance
The improvement in the trade balance was particularly sharp in March 2019 when the trade deficit narrowed by nearly 20 percent compared to March 2018, due to record high export earnings and a significant reduction in imports. This is a drastic reversal of the trend of increasing imports in 2018 and 2019.
 Imports
Imports
Expenditure on imports continued to decline due to policy measures adopted by the Central Bank and the government. Consumer, intermediate and investment goods imports decreased. The lower fuel prices were significant in intermediate imports decreasing.
Continuity
The trade deficit was only US$ 1.7 billion in the first quarter. If this trend continues, the trade deficit could decline to as little as US$ 7 billion. Even if the trade deficit is not reduced that much, but to US$ 8 billion, it could result in a significant balance of payments surplus.
Risks
However there are unpredictable factors that could affect the trade deficit adversely. The current international oil prices could rise, if the US imposes a trade embargo on Iran. Higher prices for fuel would affect the trade balance adversely. Trade tensions are serious threats to the country’s trade.
Policies
The continuation of tariff policies on gold and motor vehicle imports are necessary to stem these imports. Furthermore, there should not be a relaxation of import tariffs. Fiscal and monetary policies must be vigilant to stem imports.
Reversal
This decrease in the trade deficit in the first quarter of this year is a reversal of the trend in recent years, when despite an increase in exports, the trade deficit increased owing to a larger increase in imports. In contrast, there was a reduction in imports and a continued increase in exports that reduced the trade deficit by 12 percent in the first quarter of this year.
It is of utmost importance that this declining trend in imports continues in the next nine months to reduce the trade deficit to below US$ 9 billion.
This is especially important as the insecure conditions in the country and geopolitical factors are likely to decrease tourist earnings workers’ remittances that are the two most significant foreign exchange earnings. Foeign investments too are likely to fall.
Projection
If imports continue to be contained, the trade deficit could be brought down to around 8 to 8.5 billion that could enable a balance of payments surplus of significance. However this would be possible only if workers’ remittances and tourist earnings do not decline too much.
While a reduced trade deficit would boost the chances of a higher balance of payments, the dip in workers’ remittances and tourist earnings should not offset the gains in the trade balance. Foreign investments too are expected to decrease. Together these may reduce foreign earnings by about US$ 3 billion.
Summing up
One of the serious weaknesses of the economy has been the increasing trade deficits in recent years. The trade deficit of US$ 9.6 billion in 2018 increased to US$ 10.3 billion last year. Such a large trade deficit weakens the balance of payments and erodes the foreign exchange reserves.
The decrease in the trade deficit in the first quarter of this year was a reversal of the trend in recent years, when despite an increase in exports, the trade deficit increased owing to a larger increase in imports. In contrast, there was a reduction in imports and a continued increase in exports in the first quarter of this year.
Every effort must be made to enhance this reduction in the trade deficit to increase the balance of payments surplus.


Leave a Reply
Post Comment