What is Drug Addiction?
View(s):
Dushyantha Rathnasinghe (MBA, Pg Dip in Psychology, BSc in IT and Comm) Senior Lecturer (Nawaloka College of Higher Studies) Senior Psychological Counselor at Damrivi Foundation & Park Hospital Research Assistant at Medical Faculty University of Colombo
Addiction is a chronic disease that affects the reward structure of the brain. It is caused by neurochemical reactions that are prompted by the introduction of certain substances and behaviors. Addiction impairs a person’s judgment, physiological independence and emotional well-being. Overcoming addiction requires therapeutic intervention and ongoing support from an addiction specialist.
Addiction develops when a person becomes physically, psychologically and emotionally dependent, most often to drugs or alcohol. It is defined by a collection of unique characteristics:
A chronic inability to abstain from a certain substance or behavior
Behavioral impairment or loss of control
Cravings for a substance or behavior
Continued use of a substance, or engagement in a behavior despite evident consequences, such as financial ruin, damaged relationships or career loss
Inappropriate or dysfunctional emotional response when access to substance or behavior is removed
Alcohol or drug addiction can affect almost every aspect of an individual’s life, including their relationships, their finances and their professional endeavors. Many people who struggle with addiction experience memory impairment and physical health problems, including chronic disease and disability.
What Causes Addiction?
Addiction may refer to psychological dependencies, such as those to gambling, sex and work. The most commonly addressed form of addiction is substance abuse.
Drug and alcohol addiction include abuse to items like: Alcohol
Methamphetamines
Opioids, including Prescription Pain Medications
Stimulants
 Tobacco
Tobacco
Habits are occasionally mistaken for addiction, but there is a key difference. While often second-nature, habits are self-controlled and done by choice. Breaking a habit takes time but is not associated with the same psychological and neurological changes as addiction.
Causes of drug addiction can be due to certain lifestyle factors including: High Stress Levels
Having a parent with a history of addiction
Severe Trauma or Injury
Exposure to substance abuse at a young age
Mental health conditions, especially mood disorders such as chronic anxiety and depression
Psychological trauma, including loss of a loved one or chronic loneliness
There are a lot of different factors that can be the causes of drug addiction. The above items are what people possess when they seek addiction treatment in most cases, but not all.
Physical Nature of Addiction Addictive substances and behaviors can physically alter areas of the brain that are associated with reward, memory and motivation. Repeated use of these substances increases your risk of becoming addicted.
Areas of the brain affected by alcohol and drug addiction include: Nucleus Accumbent
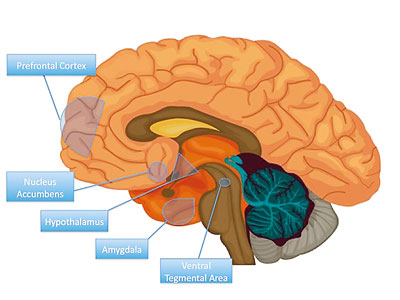 Anterior Cingulate Cortex
Anterior Cingulate Cortex
Basal Forebrain
Amygdala
Alcohol and drug addiction also physically affect the brain by interfering with the interaction of brain chemicals, or neurotransmitters, especially between the memory and reward areas of the brain.
Due to the physiological nature of drug addiction, overcoming addiction takes time and ongoing effort. Ceasing use of an addictive substance will often lead to withdrawal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting and headaches. Detoxification and addiction therapy programs are structured to control and reduce these symptoms while increasing your chances of recovery.
The Below Diagram Explains The Affected Areas of the Brian


