News
Beware of stones
 Sri Lanka is well and truly in the ‘Stone Belt’ cutting across the countries in Southeast Asia going up to South Africa.
Sri Lanka is well and truly in the ‘Stone Belt’ cutting across the countries in Southeast Asia going up to South Africa.
This is why Consultant Urologist Dr. K. Sutharshan attached to the Army Hospital in Narahenpita, who rose to fame by setting a new Guinness Record last year for removing the “largest and heaviest” stone from a kidney ever, is urging people on preventive measures as well as the need for early diagnosis and treatment.
Dr. Sutharshan set the Guinness Record in June 2023, beating an Indian record (13-cm stone) of 2004 and a Pakistani record (600-gm stone) of 2008. What he took out from the right kidney of a 62-year-old retired military man from Chilaw, in an open surgery of 1½ hours, was a double record – the stone was the heaviest in the world weighing 800 gms and the largest with a width of 13.37 cms.
“Sri Lankans, especially in the Dry Zone and southern parts of the country, are vulnerable to a high incidence of stones which may form in the urinary system,” points out this Consultant Urologist, explaining that this is due to the extreme temperature in the country; less intake of water; diets which consist of foods high in oxalates and calcium; and also excess intake of supplements high in calcium.
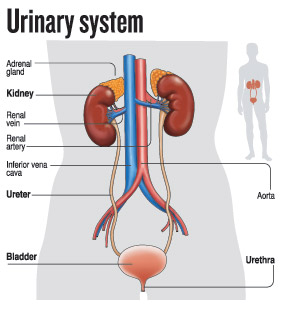
The urinary system comprises the kidneys, the ureters, the bladder and the urethra. The symptoms can vary and patients can present with:

The Guinness Record award
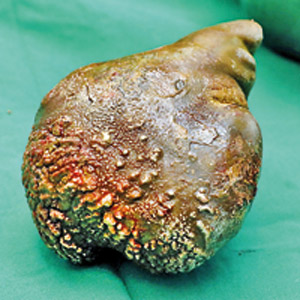
The Guinness Record stone
An obstruction of the urinary system
An infection in the urinary system
Both an obstruction and an infection
The wide and varied symptoms may include: severe pain in the lower back (acute pain from loin to groin); blood in the urine (haematuria); a burning sensation or pain when passing urine (dysuria); urine that smells bad or looks cloudy; nausea; vomiting; fever; and chills.
Dr. Sutharshan stresses that the most ‘severe’ form of stones would be ‘an obstruction and an infection’ together, with the patient being rushed to a hospital’s emergency unit with symptoms of septicaemia (blood poisoning); high fever; a drop in blood pressure; and acute renal failure. However, in diabetics, septicaemia could be masked, sans fever (afebrile).
“This is a very dangerous situation as it is dubbed ‘Silent Stones’,” he cautions, as the patient may seek treatment for other symptoms and by the time the illness is identified and followed-up, “the kidney may almost be gone”.

Dr. K. Sutharshan. Pic by M.A. Pushpa Kumara
Others may come to the Outpatients’ Department (OPD) with an obstruction sans an infection but either with normal renal function or impaired renal function, it is learnt.
In all cases, the medical assessment is vital – history, onset, duration, treatment status et al.
Going back to ‘Silent Stones’, Dr. Sutharshan says that there could be acute urine retention (a lot) in the bladder and urethra or a complete absence (nothing) of urine. On examination and palpation, the bladder would be distended. A strong pointer would be ‘renal angle tenderness’, with the patient jumping up in pain when the doctor touches the lower back.
Once the tentative diagnosis of the presence and location of stones is done, the next step would be basic tests such as urine full report (UFR) for red and pus cells); urine culture; full blood count (FBC); C-reactive protein (CRP – an increase of which would indicate inflammation in the body); electrolytes (salt, potassium and calcium which perform a variety of important functions within the body); serum creatinine (which gives an indication how well the kidneys are filtering the blood); and eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate to check how well the kidneys are working).
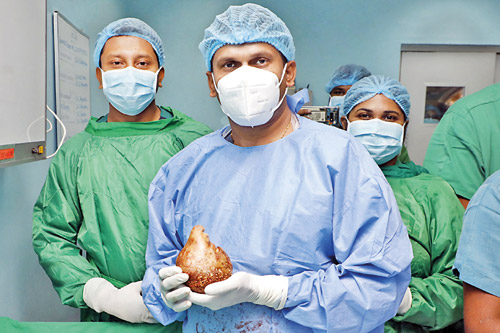
After delivery of the Guinness Record stone
Dr. Sutharshan says that if there is an elevation of serum creatinine it would be an indication of an obstruction in the urinary system. If this marker is very high, it would mean an obstruction plus an infection, along with reduced renal function.
Thereafter, a definitive identification of stones would come about through “crucial” imaging:
X-ray of the kidney, ureter and bladder (KUB) – to get the right size, site and rough density of the stone.
Ultrasound Scan (USS) of KUB – to determine whether the system is obstructed, once again site and level of obstruction and degree of hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney when it is not able to get rid of the urine collection).
Non-Contrast Computerized Tomography (NCCT) Scan of KUB – this would be for the 90-96% diagnosis of the exact size, site and density of the stone as well as the degree of obstruction
He says that with advanced stone disease some of the secondary dangers would be kidney perforation or urinoma (perinephric fluid collection, which is a collection of urine in the back of the abdomen).
With regard to treatment, Dr.Sutharshan says in the case of stone obstruction as well as an infection, it is a urological emergency, while if it is an obstruction without an infection, it is semi-urgent.
Either way, the necessity is to see a doctor immediately.
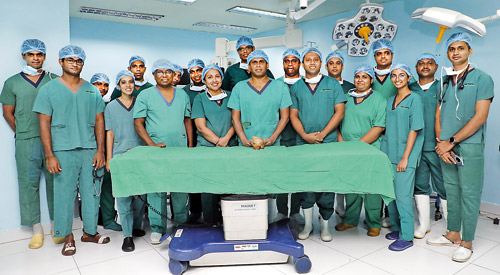
The triumphant team after delivery of the Guinness Record stone
| Stones in their variety | |
| Stones in different parts of the urinary system: Kidney stones — When chemicals in the urine harden, the result is a stone. The four types of kidney stones are calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite and cystine.The commonest stones are calcium oxalate and uric acid, while less common is struvite and rare id cystine which tends to run in families. Ureteral stones– These are kidney stones which can enter the ureters. Bladder stones– These can either form inside the bladder itself or migrate from the ureters. |
| Points to ponder | |
| An important message from Dr. K. Sutharshan: Don’t ignore stones and don’t lose out on the follow-up. Silent stones can pose much danger and the patient may quickly descend into severe illness due to septicaemia and acute renal failure. If diabetic and hypertensive, a person may have chronic renal failure. Proper diagnosis, the ideal treatment and follow-up are essential. This is why a patient should go to a Consultant Urologist. Don’t heed the many myths and fake news swirling around stones in the urinary system and their treatment.
|
The best way to say that you found the home of your dreams is by finding it on Hitad.lk. We have listings for apartments for sale or rent in Sri Lanka, no matter what locale you're looking for! Whether you live in Colombo, Galle, Kandy, Matara, Jaffna and more - we've got them all!

