|
Fighting
filariasis
This week, we look at the drugs given
for mass community treatment of filariasis ("Barawa"
or "Yaanai kaachchal). You may have taken these
two drugs in the last few months in the "National
Plan for Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis for Sri
Lanka". The target of this programme is to reduce
the worm load which leads to reduction of the transmission
of the disease and with time eliminate Filariasis from
Sri Lanka.
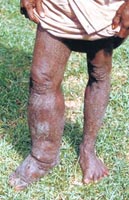 |
| A person suffering from Lymphatic
filariasis. |
The drugs used are albendazole and
diethylcarbamazine citrate (DEC). Albendazole is an
intestinal anthelminthic, and DEC an antifilarial.
- The general principles in using
medicinal drugs discussed previously apply here as
well.
- Other uses: Apart from this preventive
programme, these drugs are indicated in:
- Albendazole for treatment of worms
- Diethylcarbamazine citrate for treatment
of filarial infection (e.g.; acute lymphangitis, lymphoedema,
elephantiasis, tropical pulmonary eosinophelia). In
these instances your doctor may prescribe a longer
course of DEC (7-14 days)
- Allergy: Both drugs can cause allergic
reactions, but it is more of a problem with DEC. The
risk of allergy is high when a person has a large
load of filarial worms as the allergic reactions are
induced by disintegrating worms.
The symptoms may occur in a few hours
after taking DEC, and generally do not last for more
than three days. Symptoms include fever, headache, aches
and pains, joint pain, dizziness, malaise, vomiting,
urticaria, cough and sometimes attacks of wheezing.
Consult your doctor before taking these drugs if you
are allergic to any drugs or substances such as foods,
preservatives or dye.
If you develop the symptoms mentioned
above, or any other unusual events after taking DEC,
please seek medical advice.
- Pregnancy and breast feeding:
Pregnant women and breast feeding mothers are not
included in the mass community treatment programmes.
Albendazole is associated with foetal malformations
in animals, and the manufacturers inform that there
are no adequate and well controlled trials in human
pregnancy. Albendazole is therefore usually contra-indicated
during pregnancy. The manufacturer also cautions against
becoming pregnant while taking albendazole or within
one month of completing treatment.
- Children: Children under the age
of two years are normally excluded in the mass community
treatment programme. An important practical difficulty
in giving albendazole to young children is the size
of the tablet as there are no liquid preparations.
Hence children as young as two years have to swallow
these tablets. Albendazole is a relatively large tablet.
There is always a risk of choking when these drugs
are given unbroken to children. Parents have to make
sure that they crush the tablets and give them as
powder to young children.
- Drug interactions: Though there
are no documented drug interactions with these drugs,
it is preferable to seek advice from your doctor if
you are taking some other drugs (including over the
counter preparations, cough medicines, herbal remedies,
nutraceuticals).
- Other medical conditions: Elderly
and debilitated patients especially those with cardiac
and renal failure are excluded from mass community
treatment programmes.
Precautions
- Drowsiness and dizziness: Some
people can get dizzy or drowsy or both due to DEC.
Avoid driving and operating machines if you have this
side effect of the drug.
- Patients with allergic tendency:
Seek medical advice before you take DEC (see above).
- Side effects: Along with its beneficial
effects, any medicine may cause some unwanted side
effects. These drugs are not exceptions.
- Albendazole: Headache, stomach upsets,
diarrhoea, abdominal pain, allergic reactions
- Diethylcarbamazine citrate: Headache,
drowsiness, dizziness, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting,
lethargy, loss of appetite (most of these reactions
begin within 1 to 2 hours of taking DEC, and persist
for a few hours) allergic reactions (see above), reversible
proteinuria (passing protein in urine).
- Local reactions: Nodules (due to
dead adult worms) may appear in the groin area.
Other side effects not listed above
may also occur in some patients. If you have noticed
any other unwanted effects when taking these drugs,
inform Info Vig.
Info-Vig, Department of Pharmacology
(PO Box 271, Kynsey Road, Colombo 8 - TP Number 5677244)
monitors adverse drug reactions (side effects). Reporting
suspected adverse drug reaction to Info -Vig will help
in monitoring the drug safety in Sri Lanka.
Information provided by Dr. Shalini
Sri Ranganathan, Senior Lecturer and Professor Rohini
Fernandopulle, Department of Pharmacology, University
of Colombo. |
